Quantification of uncertainty in robot pose errors and calibration of reliable compensation values
Published in March 13, 2024
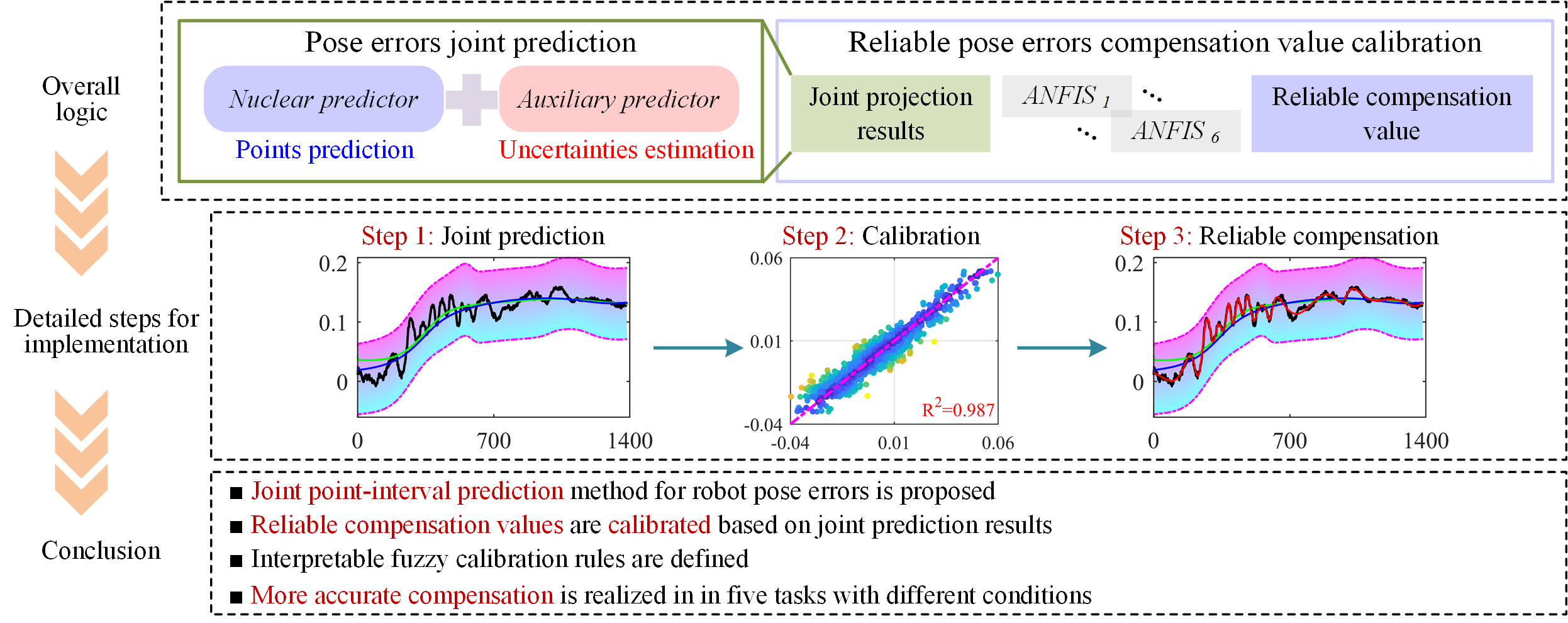
Contribution
In this paper, quantification of uncertainty in robot pose errors and calibration of reliable compensation values are proposed, which focus on the characteristics of robotic systems with multiple error sources and strong uncertainty, to bridge the current prediction and compensation paradigm that relies on point estimation. This method enables the quantification of the possible intervals of the prediction results and the improvement of the accuracy of the compensation value based on it. Overall, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- A joint point-interval prediction method is proposed in this paper. With the help of an asynchronous start-up strategy, the quantification of the uncertainty interval of the robot’s pose errors is achieved with the help of two components, the nuclear predictor and the auxiliary predictor, without affecting the accuracy of the point prediction. This provides data support for subsequent error compensation.
- Based on the joint point-interval prediction results, a reliable compensation value calibration method is proposed. The proposed method not only realizes the accuracy improvement of point prediction, but also the priority interpretation of the calibration for the compensation values is achieved with the help of fuzzy logic.
- The proposed method is validated in five tasks including space motions, constant load and milling processing. By the proposed method, the accuracy of pose errors prediction is significantly improved, which provides a strong support for the subsequent compensation. In addition, after the validation through online compensation, the maximum reduction of the pose errors reaches 90% and the minimum is more than 70%.
Graphic Abstracts
The graphic abstract is shown below
Recommended citation: T. Zhang, F. Peng, R. Yan, X. Tang, R. Deng, J. Yuan, Quantification of uncertainty in robot pose errors and calibration of reliable compensation values, Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf., 89 (2024) 102765, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2024.102765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2024.102765
